Single Table Designer
The SenseDeep Single Table Designer provides an easy, intuitive interface to create, manage and modify your single-table schemas.
Single-table schemas control how your application data are stored in DynamoDB tables. Schemas define your application entities, table indexes and key parameters. Via schemas, complex mapped table items can be more clearly and reliably accessed, modified and presented.
The designer stores your single-table schemas in your DynamoDB table. In this manner, your table is self-describing as to how table data should be interpreted. You can export schemas and generate JSON, JavaScript or TypeScript data/code to import into your apps.
The SenseDeep single-table designer works best with the OneTable library, but should work with any consistent single-table design.
For a quick overview, read SenseDeep Single Table Designer.
Setup
To use the SenseDeep single-table designer you can either create the schema by clicking the “Add Schema” button or you can create a schema from code by using the migration manager. See Migration Manager for details.
Naming and Versioning
Schemas are named and versioned. The default schema is called the Current schema. Other schemas can have any name of your choosing. For example “Prototype”.
Schemas have version numbers so that data migrations can utilize the correct versioned schema when upgrading or downgrading data items in your table. The migration manager will select and apply the correct versioned schema when data migrations are run.
Version numbers use Semantic Versioning to indicate and control data compatibility.
Schemas
The schema list displays the schemas defined in your table. You can click on “Add Schema” to create a new schema.
When adding or modifying a schema, you can define the following schema properties:
- Name — Identifying name of the schema.
- Version — SemVer compliant version of the schema.
- Type Field — The DynamoDB attribute that specifies the model type.
- ISO Dates — Whether to store dates as ISO strings vs Unix epoch dates.
- Store Nulls — Whether to store nulls in attributes vs removing null attribute values.
- Timestamps — Whether to store ‘created’ and ‘updated’ timestamps automatically in data items.
The Type field determines which entity model a data item is based upon. By default, this is set to “_type” to distinguish from your normal attributes.
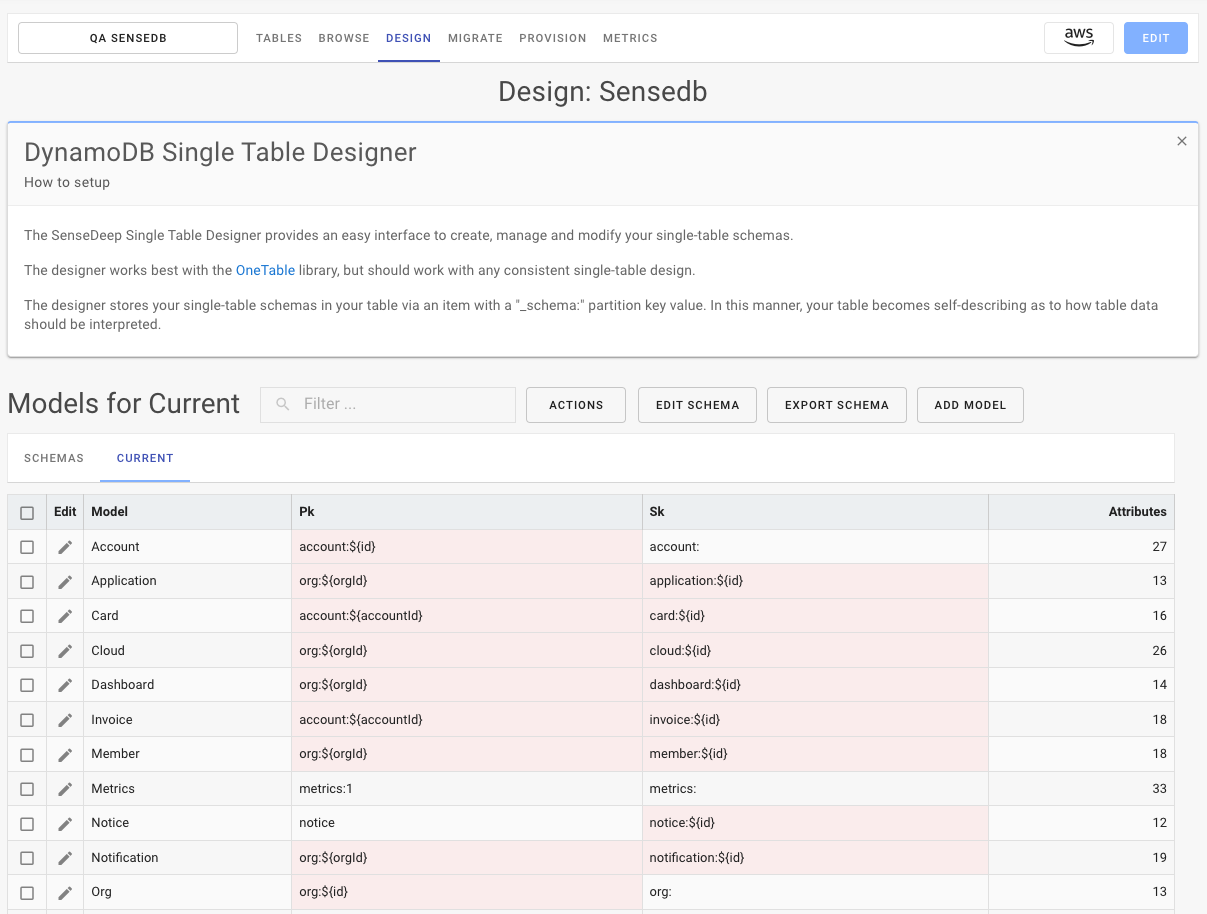
Clicking on a schema in the schema list will display the entity models defined for that schema.
Entity Models
An entity model defines the valid set of attributes for an application entity. The model list displays the available models and the primary partition and sort key used for that model as well as the number of attributes.
Clicking on a model in the list of entity models will display the entity fields (attributes) for that model. Click on “Add Model” to add a new entity model.
Via the Edit Schema button you can modify the schema name or version. If the schema is a non-current schema, you can also click Apply to Current to apply the contents of the displayed schema to the saved Current schema in the table. This overwrites the previous Current schema.
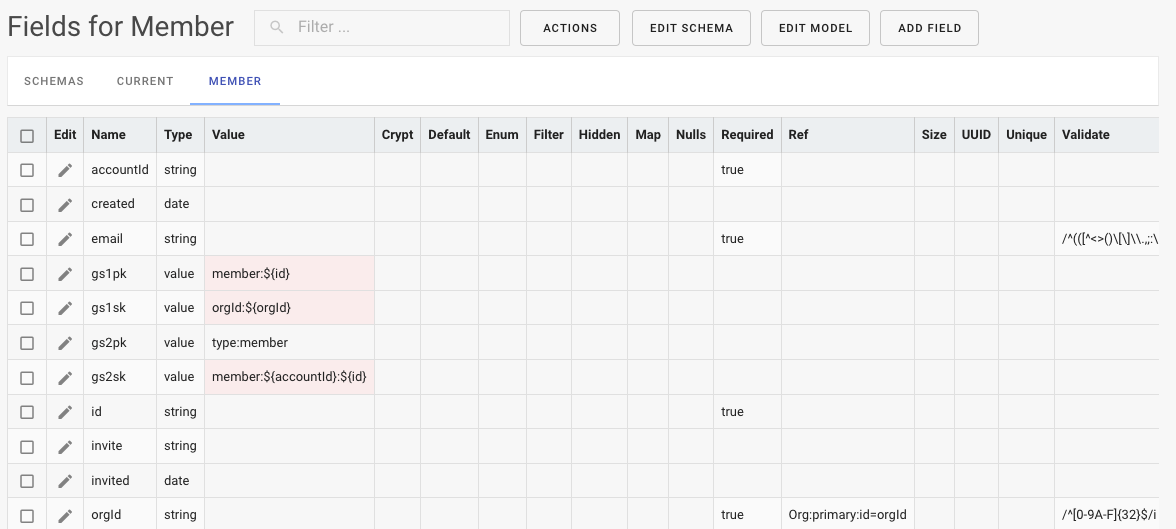
Entity Fields
Each entity field (attribute) has a defined name, type and a set of properties that may be utilized by your DynamoDB access library such as OneTable or an ORM of your choosing.
Clicking on an entity attribute will display a slide out panel to edit the properties of that DynamoDB attribute.
You can modify the type and any other properties of the field. NOTE: These properties are defined in the schema and may (or may not) be implemented or managed by your DynamoDB access library. All these properties are implemented by OneTable.
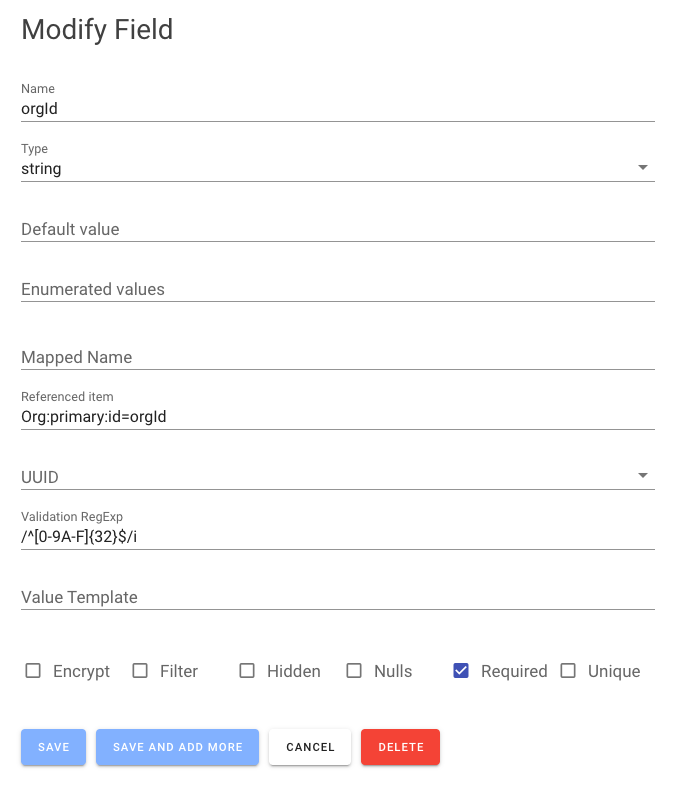
The properties include:
- Name — the name of the attribute.
- Default Value — a default value to set if not defined when created.
- Enumerated values — a list of possible values for the attribute.
- Encrypt — hint the attribute should have an extra layer of encryption.
- Filter — indicates the attribute can be used in filter expressions.
- Hidden — the attribute should be hidden in query results by default.
- Mapped Name — a shorter real attribute name when storing in the table.
- Nulls — indicates that nulls should be stored in the table vs being removed.
- Required — the attribute is required to be present when created.
- Data Type — the attribute data type.
- Validation Expression — a regular expression to validate all writes to the table.
- Value template — a JavaScript value template to compose the attribute based on other attribute values.
- Unique — indicates the attribute must always hold a unique value over all such items.
Export
You can also export your schema in JavaScript, TypeScript or JSON formats via the Export Schema button from the Models list. You can utilize the exported file directly in your OneTable apps to control your database interactions.